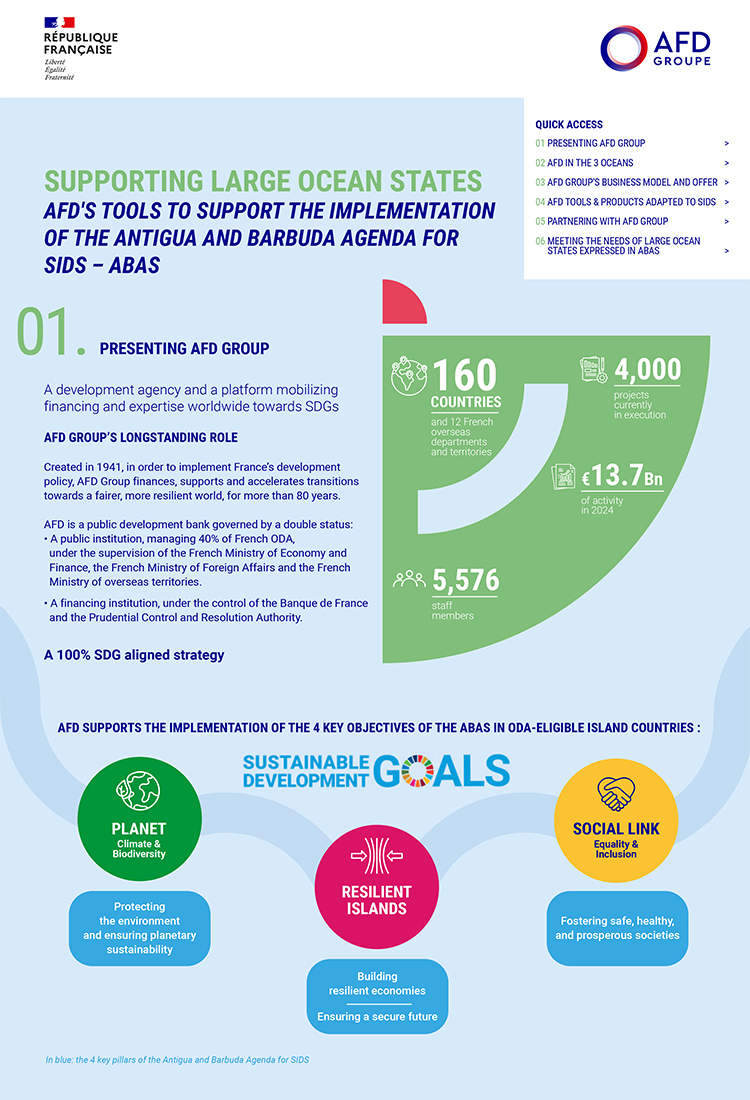
Share the page
Papua New Guinea
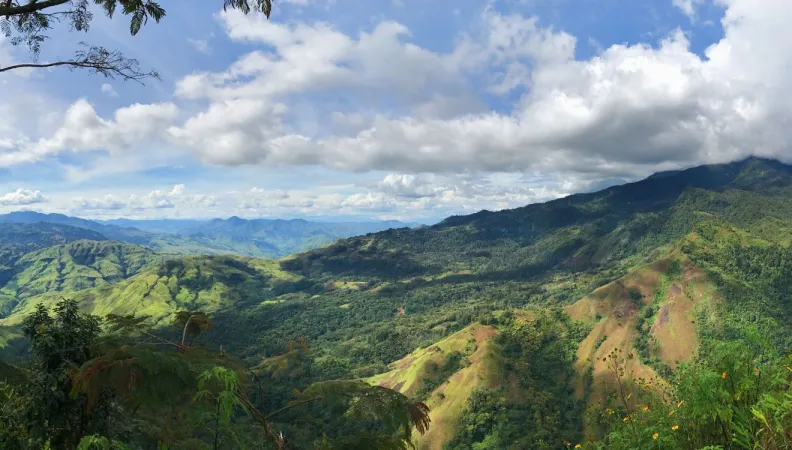

Representing 80% of the total population of the Pacific Islands and home to one of the world's most important biodiversity refuges, Papua New Guinea is a key partner for AFD Group. This partnership, focusing on climate and biodiversity, is in full swing: a first bilateral agreement was signed in July 2023, along with two letters of intent (energy transition, greening of port infrastructures, and green funding). Expertise France also opened an office there.
Context
Located north of Australia, Papua New Guinea is the largest, most populous country in the Pacific, with 9 million inhabitants on a territory of 462,840 km2.
Comprising the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, the Bismarck Archipelago, Bougainville Island, and numerous smaller islands, Papua New Guinea features great geographical and cultural diversity. There are almost 850 indigenous languages and an even greater number of clans, many of which live in isolated regions (85% of the population live in rural areas).
What's more, forests, which make up 78% of the country, are a vital source of food security for many inhabitants and an essential part of the country's cultural, linguistic, and spiritual make-up.
Economically, Papua New Guinea is classified as a lower-middle-income country with a GDP of around 24.7 billion dollars in 2020. But it has the highest level of income inequality in the Asia-Pacific region and ranks 155th in the world in the 2019 UN Human Development Index.
The country is highly exposed to natural and climate risks: in 2021, it ranked 9th out of 181 countries on the World Risk Index.
With a commitment to operate in Papua New Guinea since 2018, AFD Group supports the country in its sustainable development objectives and in the fight against climate change. A renewed commitment during French President Emmanuel Macron's visit in July 2023.
The Group's action in the country, which is in line with the country's major development challenges and the Pacific Islands Forum's (PIF) 2050 strategy for the Blue Pacific, focuses on the following four areas:
- management and resilience of marine and coastal ecosystems;
- protecting forests;
- development and greening of financial systems;
- energy transition.
Until now, AFD has only provided grants for regional projects and specific grant tools (FEXTE). However, lending activities are set to expand in the years ahead.
AFD's activities in Papua New Guinea are overseen by the Pacific Ocean Regional Office.
Our approach
"AFD GROUP AND PAPUA NEW GUINEA: STRENGTHENING CLIMATE RESILIENCE"
Papua New Guinea is one of 19 Pacific island states and territories covered by the Kiwa Initiative, which supports projects focusing on Nature-based Solutions to enhance adaptation to the effects of climate change. The country has several projects in the pipeline:
- The regional project "Nature-based solutions in Melanesian watersheds to generate co-benefits for climate resilience, biodiversity, health and well-being (Wish+)". Supported by Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), the project aims to promote the safe management of drinking water, sanitation, and wastewater in the central forest of Manus Island.
- The local project run by KGWan Eco Habitat Inc. aims to improve livelihoods through biodiversity conservation and sustainable climate systems in the mountainous region of Simbu. This project aims to help the rural communities of the Inaugl tribe to participate in managing natural resources to combat deforestation and soil degradation.
- Technical assistance provided by the Pacific Community (SPC) and the Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP) supports member territories in developing regional project proposals for submission to the Kiwa Initiative.
Papua New Guinea is home to one of the world's largest primary forests. The environmental protection of this forest and the promotion of greener sources of social and economic development are a priority for the Papuan government.
In July 2023, the European Union entrusted Expertise France with the task of implementing the largest component of a major project concerning forests and biodiversity. The 33.5 million euro Forest, Climate, and Biodiversity Protection (FCCB) program aims to support a development model that reconciles forestry, climate change, and biodiversity with green growth and sustainable, inclusive, gender-sensitive jobs.
In addition to the FCCB project, France is also supporting the creation of a Country Package. The aim is to help mobilize funds from the international community to help Papua achieve the 30% target for protected areas on land and at sea by 2030 (the 30x30 target). Initially, Expertise France will deploy an international technical expert and technical assistance to the Papua government taskforce.
These two projects show the determination of Team Europe to support the country's efforts in this area.
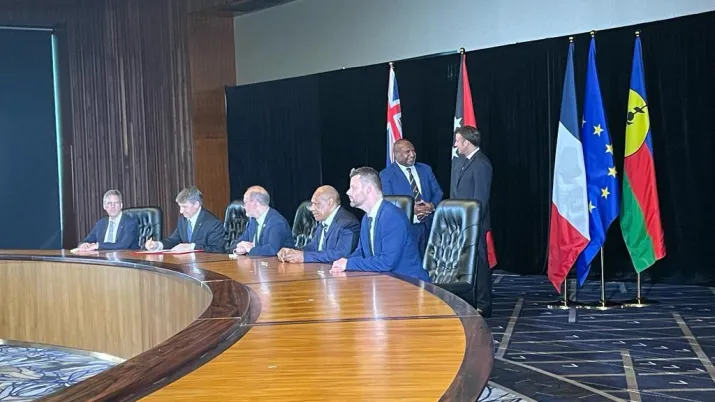
In July 2023, AFD signed a letter of intent with the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI) and the Bank of Papua New Guinea. The aim is to support the establishment of a center for green finance in Papua New Guinea and to facilitate the implementation of the national green taxonomy.
This collaboration will also aim to identify gaps and propose financial tools to national financial players to encourage them to commit to an ecological and energy transition.
AFD will also be supporting the greening of financial systems in the Pacific with the GGGI starting in 2024. This approach is aimed at supporting island states facing the staggering costs of natural disasters on their economies (5% of regional GDP per year, i.e. dollars of 1 billion).
By 2021, 20% of Papua New Guinea's population had access to electricity. The country is dependent on fossil fuels (70% of the energy mix).
In July 2023, AFD signed its first funding agreement to support the country's energy transition. This technical cooperation involves AFD, the New Caledonian state-owned energy company Enercal and Papua New Guinea's PNG Power Limited. It aims to promote renewable energy integration into the national power grid by mobilizing New Caledonian expertise.
Alongside the European Commission, the EIB, and the Australian government's Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT), AFD signed a letter of intent in July 2023 to support the rehabilitation of the Port of Rabaul and the development of a "green port strategy" for PNG Ports Corporation Ltd. AFD will be providing a grant of 500 000 euros to conduct a feasibility study for this project.
The goal is to support an eco-friendly model for the port's infrastructure that covers waste and wastewater management, greenhouse gas emissions, and the resilience of the infrastructure itself. Project funding could be provided by AFD, alongside the EIB and the European Union Delegation.
In the field
News & Press Releases
AFD Group in Papua New Guinea: Boosting Biodiversity Protection to help Island States Cope with Climate Change
With the opening of its Expertise France subsidiary in Papua New Guinea and AFD's first bilateral agreement with the country, AFD Group signals its commitment to the preservation of forests, biodivers...

Publications & Media


Key figures
-
5 new AFD Group projects planned for 2023-2024
-
4.8 million euros committed via the Kiwa Initiative
